Sewage Treatment Plant
A sewage treatment plant (STP) is a facility designed to treat and process domestic and industrial wastewater, commonly known as sewage or wastewater, before it is discharged into the environment or reused for various purposes. The primary goal of sewage treatment plants is to remove pollutants, contaminants, and harmful substances from the wastewater, making it safe for the environment and public health.
The typical sewage treatment process in a sewage treatment plant involves several stages:
Preliminary Treatment: The incoming raw sewage undergoes preliminary treatment to remove large solid objects, such as sticks, rags, plastic, and other debris. This process includes screening and grit removal to protect downstream equipment and prevent clogging.
Primary Treatment: In the primary treatment stage, the wastewater flows into large sedimentation tanks, called primary clarifiers. In these tanks, the flow velocity is reduced, allowing heavier solids and organic matter to settle at the bottom as primary sludge. The clarified water at the top, known as primary effluent, moves on to the next treatment stage.
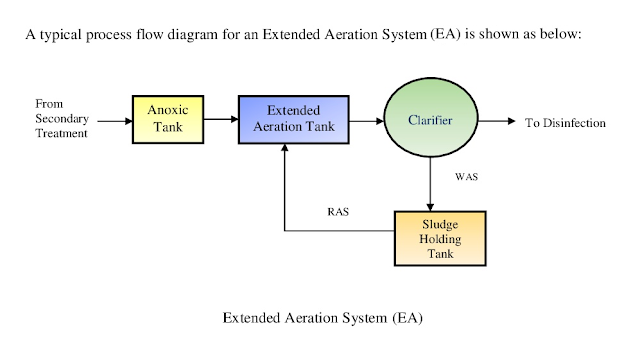
Secondary Treatment (Biological Treatment): After primary treatment, the primary effluent enters the secondary treatment stage, which primarily involves biological processes. The most common secondary treatment method is the activated sludge process. In this process, the wastewater is mixed with microorganisms (activated sludge) in aeration tanks. These microorganisms consume organic matter, further breaking it down into carbon dioxide, water, and more microbial biomass. The treated water, known as secondary effluent, is then sent for further treatment or discharge.
Tertiary Treatment (Advanced Treatment): Depending on the required water quality standards or potential reuse purposes, tertiary treatment may be applied. Tertiary treatment employs advanced processes such as additional filtration, disinfection (chlorination, UV radiation, or ozonation), and nutrient removal (like phosphorus and nitrogen removal) to achieve the desired water quality.
Sludge Treatment: Throughout the treatment process, solid materials (primary and secondary sludge) accumulate and are collected. The sludge undergoes further treatment processes, including thickening, dewatering, and stabilization, to reduce volume and make it suitable for disposal or beneficial reuse as biosolids.
Effluent Discharge or Reuse: The treated wastewater, now known as effluent, is either discharged into nearby water bodies like rivers, lakes, or oceans if it meets regulatory standards for discharge, or it undergoes further treatment for specific reuse applications, such as irrigation, industrial processes, or groundwater recharge.
Sewage Treatment Plant plays a vital role in protecting public health, safeguarding the environment from water pollution, and ensuring sustainable management of water resources. The process employed in a sewage treatment plant may vary based on the scale of the plant, local regulations, and the specific requirements for effluent quality and reuse.

This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteExceptional content! Insightful and well-presented. Thank you for sharing valuable information.
ReplyDeleteReady to transform the way you manage sewage with water design technologies? Contact us today and embrace a future of sustainable wastewater solutions with our advanced Sewage Treatment Plant in Gujarat.